🐸Coqui.ai News#
📣 ⓍTTSv2 is here with 16 languages and better performance across the board.
📣 ⓍTTS fine-tuning code is out. Check the example recipes.
📣 ⓍTTS can now stream with <200ms latency.
📣 ⓍTTS, our production TTS model that can speak 13 languages, is released Blog Post, Demo, Docs
📣 🐶Bark is now available for inference with unconstrained voice cloning. Docs
📣 You can use ~1100 Fairseq models with 🐸TTS.
📣 🐸TTS now supports 🐢Tortoise with faster inference. Docs
📣 Voice generation with prompts - Prompt to Voice - is live on Coqui Studio!! - Blog Post
📣 Voice generation with fusion - Voice fusion - is live on Coqui Studio.
📣 Voice cloning is live on Coqui Studio.

 #
#
🐸TTS is a library for advanced Text-to-Speech generation.
🚀 Pretrained models in +1100 languages.
🛠️ Tools for training new models and fine-tuning existing models in any language.
📚 Utilities for dataset analysis and curation.
💬 Where to ask questions#
Please use our dedicated channels for questions and discussion. Help is much more valuable if it’s shared publicly so that more people can benefit from it.
Type |
Platforms |
|---|---|
🚨 Bug Reports |
|
🎁 Feature Requests & Ideas |
|
👩💻 Usage Questions |
|
🗯 General Discussion |
🔗 Links and Resources#
Type |
Links |
|---|---|
💼 Documentation |
|
💾 Installation |
|
👩💻 Contributing |
|
📌 Road Map |
|
🚀 Released Models |
|
📰 Papers |
🥇 TTS Performance#
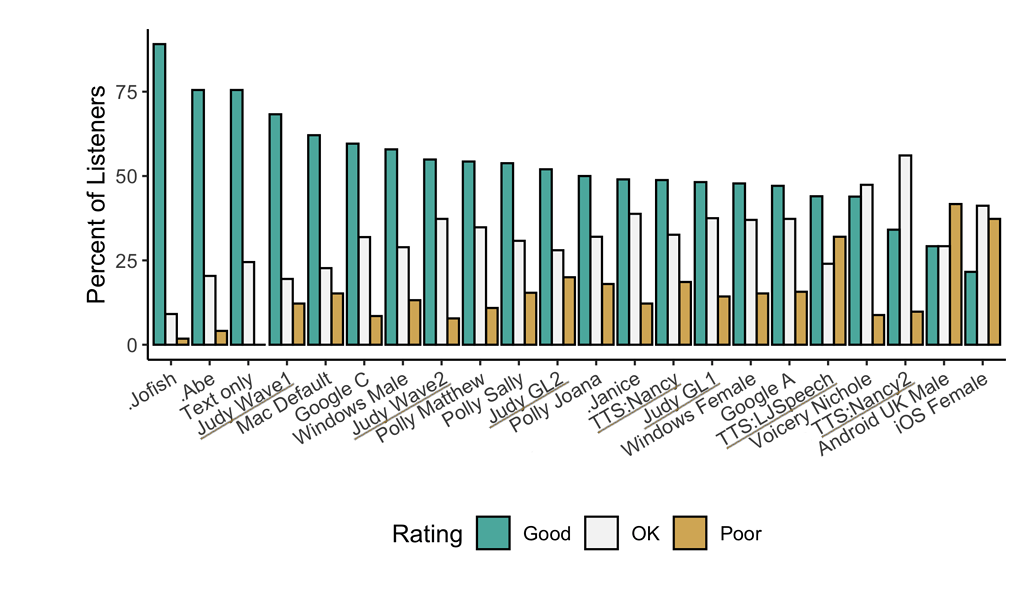
Underlined “TTS*” and “Judy*” are internal 🐸TTS models that are not released open-source. They are here to show the potential. Models prefixed with a dot (.Jofish .Abe and .Janice) are real human voices.
Features#
High-performance Deep Learning models for Text2Speech tasks.
Text2Spec models (Tacotron, Tacotron2, Glow-TTS, SpeedySpeech).
Speaker Encoder to compute speaker embeddings efficiently.
Vocoder models (MelGAN, Multiband-MelGAN, GAN-TTS, ParallelWaveGAN, WaveGrad, WaveRNN)
Fast and efficient model training.
Detailed training logs on the terminal and Tensorboard.
Support for Multi-speaker TTS.
Efficient, flexible, lightweight but feature complete
Trainer API.Released and ready-to-use models.
Tools to curate Text2Speech datasets under
dataset_analysis.Utilities to use and test your models.
Modular (but not too much) code base enabling easy implementation of new ideas.
Model Implementations#
Spectrogram models#
End-to-End Models#
ⓍTTS: blog
VITS: paper
🐸 YourTTS: paper
🐢 Tortoise: orig. repo
🐶 Bark: orig. repo
Attention Methods#
Speaker Encoder#
Vocoders#
Voice Conversion#
FreeVC: paper
You can also help us implement more models.
Installation#
🐸TTS is tested on Ubuntu 18.04 with python >= 3.9, < 3.12..
If you are only interested in synthesizing speech with the released 🐸TTS models, installing from PyPI is the easiest option.
pip install TTS
If you plan to code or train models, clone 🐸TTS and install it locally.
git clone https://github.com/coqui-ai/TTS
pip install -e .[all,dev,notebooks] # Select the relevant extras
If you are on Ubuntu (Debian), you can also run following commands for installation.
$ make system-deps # intended to be used on Ubuntu (Debian). Let us know if you have a different OS.
$ make install
If you are on Windows, 👑@GuyPaddock wrote installation instructions here.
Docker Image#
You can also try TTS without install with the docker image. Simply run the following command and you will be able to run TTS without installing it.
docker run --rm -it -p 5002:5002 --entrypoint /bin/bash ghcr.io/coqui-ai/tts-cpu
python3 TTS/server/server.py --list_models #To get the list of available models
python3 TTS/server/server.py --model_name tts_models/en/vctk/vits # To start a server
You can then enjoy the TTS server here More details about the docker images (like GPU support) can be found here
Synthesizing speech by 🐸TTS#
🐍 Python API#
Running a multi-speaker and multi-lingual model#
import torch
from TTS.api import TTS
# Get device
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
# List available 🐸TTS models
print(TTS().list_models())
# Init TTS
tts = TTS("tts_models/multilingual/multi-dataset/xtts_v2").to(device)
# Run TTS
# ❗ Since this model is multi-lingual voice cloning model, we must set the target speaker_wav and language
# Text to speech list of amplitude values as output
wav = tts.tts(text="Hello world!", speaker_wav="my/cloning/audio.wav", language="en")
# Text to speech to a file
tts.tts_to_file(text="Hello world!", speaker_wav="my/cloning/audio.wav", language="en", file_path="output.wav")
Running a single speaker model#
# Init TTS with the target model name
tts = TTS(model_name="tts_models/de/thorsten/tacotron2-DDC", progress_bar=False).to(device)
# Run TTS
tts.tts_to_file(text="Ich bin eine Testnachricht.", file_path=OUTPUT_PATH)
# Example voice cloning with YourTTS in English, French and Portuguese
tts = TTS(model_name="tts_models/multilingual/multi-dataset/your_tts", progress_bar=False).to(device)
tts.tts_to_file("This is voice cloning.", speaker_wav="my/cloning/audio.wav", language="en", file_path="output.wav")
tts.tts_to_file("C'est le clonage de la voix.", speaker_wav="my/cloning/audio.wav", language="fr-fr", file_path="output.wav")
tts.tts_to_file("Isso é clonagem de voz.", speaker_wav="my/cloning/audio.wav", language="pt-br", file_path="output.wav")
Example voice conversion#
Converting the voice in source_wav to the voice of target_wav
tts = TTS(model_name="voice_conversion_models/multilingual/vctk/freevc24", progress_bar=False).to("cuda")
tts.voice_conversion_to_file(source_wav="my/source.wav", target_wav="my/target.wav", file_path="output.wav")
Example voice cloning together with the voice conversion model.#
This way, you can clone voices by using any model in 🐸TTS.
tts = TTS("tts_models/de/thorsten/tacotron2-DDC")
tts.tts_with_vc_to_file(
"Wie sage ich auf Italienisch, dass ich dich liebe?",
speaker_wav="target/speaker.wav",
file_path="output.wav"
)
Example text to speech using Fairseq models in ~1100 languages 🤯.#
For Fairseq models, use the following name format: tts_models/<lang-iso_code>/fairseq/vits.
You can find the language ISO codes here
and learn about the Fairseq models here.
# TTS with on the fly voice conversion
api = TTS("tts_models/deu/fairseq/vits")
api.tts_with_vc_to_file(
"Wie sage ich auf Italienisch, dass ich dich liebe?",
speaker_wav="target/speaker.wav",
file_path="output.wav"
)
Command-line tts#
Synthesize speech on command line.
You can either use your trained model or choose a model from the provided list.
If you don’t specify any models, then it uses LJSpeech based English model.
Single Speaker Models#
List provided models:
$ tts --list_models
Get model info (for both tts_models and vocoder_models):
Query by type/name: The model_info_by_name uses the name as it from the –list_models.
$ tts --model_info_by_name "<model_type>/<language>/<dataset>/<model_name>"
For example:
$ tts --model_info_by_name tts_models/tr/common-voice/glow-tts $ tts --model_info_by_name vocoder_models/en/ljspeech/hifigan_v2
Query by type/idx: The model_query_idx uses the corresponding idx from –list_models.
$ tts --model_info_by_idx "<model_type>/<model_query_idx>"
For example:
$ tts --model_info_by_idx tts_models/3
Query info for model info by full name:
$ tts --model_info_by_name "<model_type>/<language>/<dataset>/<model_name>"
Run TTS with default models:
$ tts --text "Text for TTS" --out_path output/path/speech.wav
Run TTS and pipe out the generated TTS wav file data:
$ tts --text "Text for TTS" --pipe_out --out_path output/path/speech.wav | aplay
Run a TTS model with its default vocoder model:
$ tts --text "Text for TTS" --model_name "<model_type>/<language>/<dataset>/<model_name>" --out_path output/path/speech.wav
For example:
$ tts --text "Text for TTS" --model_name "tts_models/en/ljspeech/glow-tts" --out_path output/path/speech.wav
Run with specific TTS and vocoder models from the list:
$ tts --text "Text for TTS" --model_name "<model_type>/<language>/<dataset>/<model_name>" --vocoder_name "<model_type>/<language>/<dataset>/<model_name>" --out_path output/path/speech.wav
For example:
$ tts --text "Text for TTS" --model_name "tts_models/en/ljspeech/glow-tts" --vocoder_name "vocoder_models/en/ljspeech/univnet" --out_path output/path/speech.wav
Run your own TTS model (Using Griffin-Lim Vocoder):
$ tts --text "Text for TTS" --model_path path/to/model.pth --config_path path/to/config.json --out_path output/path/speech.wav
Run your own TTS and Vocoder models:
$ tts --text "Text for TTS" --model_path path/to/model.pth --config_path path/to/config.json --out_path output/path/speech.wav --vocoder_path path/to/vocoder.pth --vocoder_config_path path/to/vocoder_config.json
Multi-speaker Models#
List the available speakers and choose a <speaker_id> among them:
$ tts --model_name "<language>/<dataset>/<model_name>" --list_speaker_idxs
Run the multi-speaker TTS model with the target speaker ID:
$ tts --text "Text for TTS." --out_path output/path/speech.wav --model_name "<language>/<dataset>/<model_name>" --speaker_idx <speaker_id>
Run your own multi-speaker TTS model:
$ tts --text "Text for TTS" --out_path output/path/speech.wav --model_path path/to/model.pth --config_path path/to/config.json --speakers_file_path path/to/speaker.json --speaker_idx <speaker_id>
Voice Conversion Models#
$ tts --out_path output/path/speech.wav --model_name "<language>/<dataset>/<model_name>" --source_wav <path/to/speaker/wav> --target_wav <path/to/reference/wav>
Directory Structure#
|- notebooks/ (Jupyter Notebooks for model evaluation, parameter selection and data analysis.)
|- utils/ (common utilities.)
|- TTS
|- bin/ (folder for all the executables.)
|- train*.py (train your target model.)
|- ...
|- tts/ (text to speech models)
|- layers/ (model layer definitions)
|- models/ (model definitions)
|- utils/ (model specific utilities.)
|- speaker_encoder/ (Speaker Encoder models.)
|- (same)
|- vocoder/ (Vocoder models.)
|- (same)
Documentation Content#
Get started
- Tutorial For Nervous Beginners
- Installation
- Humble FAQ
- Errors with a pre-trained model. How can I resolve this?
- What are the requirements of a good 🐸TTS dataset?
- How should I choose the right model?
- How can I train my own
ttsmodel? - How can I train in a different language?
- How can I train multi-GPUs?
- How can I check model performance?
- How do I know when to stop training?
- My model does not learn. How can I debug?
- Attention does not align. How can I make it work?
- How can I test a trained model?
- My Tacotron model does not stop - I see “Decoder stopped with ‘max_decoder_steps” - Stopnet does not work.
- Contribution guidelines
Using 🐸TTS
- Synthesizing Speech
- Docker images
- Basic inference
- Start a server
- Implementing a Model
- Template 🐸TTS Model implementation
- Implementing a New Language Frontend
- Training a Model
- Multi-speaker Training
- Fine-tuning a 🐸 TTS model
- Configuration
- Formatting Your Dataset
- What makes a good TTS dataset
- TTS Datasets
- Mary-TTS API Support for Coqui-TTS
Main Classes
`tts` Models

